给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
分治和优先队列需要在看一下
示例1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| 输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
|
示例2:
错误解法
思路1:
先判断非空情况,若不为空,则利用题21的解法依次比较两个链表,实践表明这种方法虽然可以用,但是会超时,解法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if l1 == None and l2 == None:
return None
elif l1 != None and l2 == None:
return l1
elif l1 == None and l2 != None:
return l2
if l1.val < l2.val:
res = ListNode(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
else:
res = ListNode(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
p = res
while l1 or l2:
if l1 == None and l2 != None:
p.next = l2
break
elif l2 == None and l1 != None:
p.next = l1
break
else:
if l1.val < l2.val:
p.next = ListNode(l1.val)
p = p.next
l1 = l1.next
else:
p.next = ListNode(l2.val)
p = p.next
l2 = l2.next
return res
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
if len(lists) == 0:
return None
elif len(lists) == 1 and type(lists) == None :
return []
res = lists[0]
for temp in lists[1:]:
res = self.mergeTwoLists(res,temp)
return res
|
正确解法
需要使用c++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode *a, ListNode *b) {
if ((!a) || (!b)) return a ? a : b;
ListNode head, *tail = &head, *aPtr = a, *bPtr = b;
while (aPtr && bPtr) {
if (aPtr->val < bPtr->val) {
tail->next = aPtr; aPtr = aPtr->next;
} else {
tail->next = bPtr; bPtr = bPtr->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = (aPtr ? aPtr : bPtr);
return head.next;
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
ListNode *ans = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < lists.size(); ++i) {
ans = mergeTwoLists(ans, lists[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
|
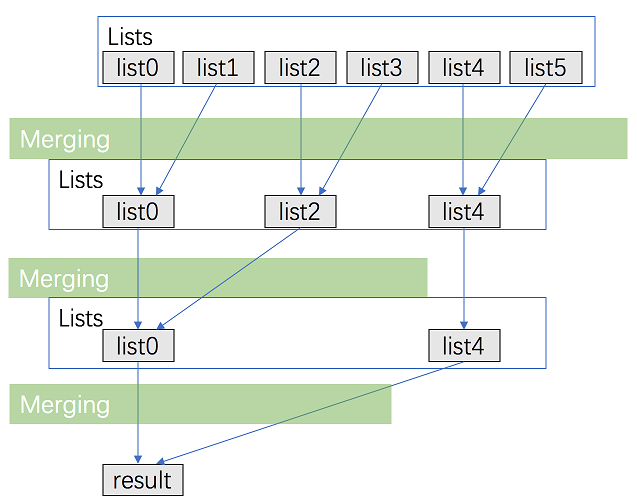
方法二:分治
考虑优化方法一,用分治的方法进行合并。
- 将 $k$ 个链表配对并将同一对中的链表合并;
- 第一轮合并以后,$k$个链表被合并成了$\frac{k}{2}$个链表,平均长度为$\frac{2n}{k}$,然后是$\frac{k}{4}$,$\frac{k}{8}$个链表等等
- 重复这一过程,直到得到了最终的有序链表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| ListNode* merge(vector <ListNode*> &lists, int l, int r) {
if(l==r) return lists[l];
if(l>r) return nullptr;
int mid = (l+r) >> 1;
return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists,l,mid),merge(lists,mid+1,r));
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
return merge(lists,0,lists.size()-1);
}
|
方法三:优先队列
这个方法和前两种方法的思路有所不同,我们需要维护当前每个链表没有被合并的元素的最前面一个,
$k$个链表就最多有$k$个满足这样条件的元素,每次在这些元素里面选取 val 属性最小的元素合并到答案中。
选取最小元素的时候,我们可以用优先队列来优化这个过程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| struct Status {
int val;
ListNode *ptr;
bool operator < (const Status &rhs) const {
return val > rhs.val;
}
};
priority_queue <Status> q;
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
for (auto node: lists) {
if (node) q.push({node->val, node});
}
ListNode head, *tail = &head;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto f = q.top(); q.pop();
tail->next = f.ptr;
tail = tail->next;
if (f.ptr->next)
q.push({f.ptr->next->val, f.ptr->next});
}
return head.next;
}
|
c++优先队列:
普通的队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,元素在队列尾追加,而从队列头删除。
在优先队列中,元素被赋予优先级。当访问元素时,具有最高优先级的元素最先删除。优先队列具有最高级先出 (first in, largest out)的行为特征。


